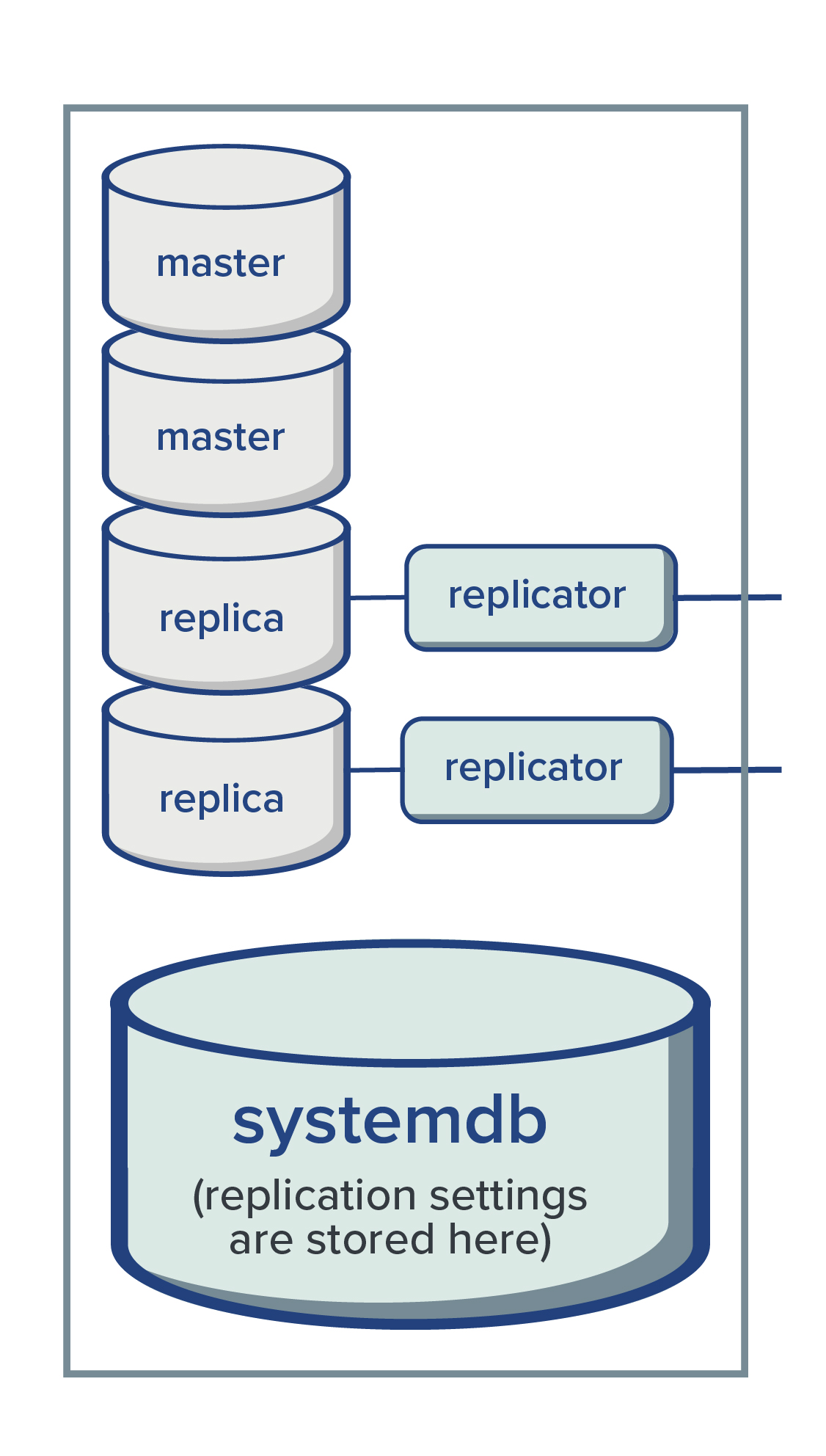
Replication
Replication strategy
immudb includes support for replication by means of a follower approach. A database can be created or configured either to be a master or a replica of another database.
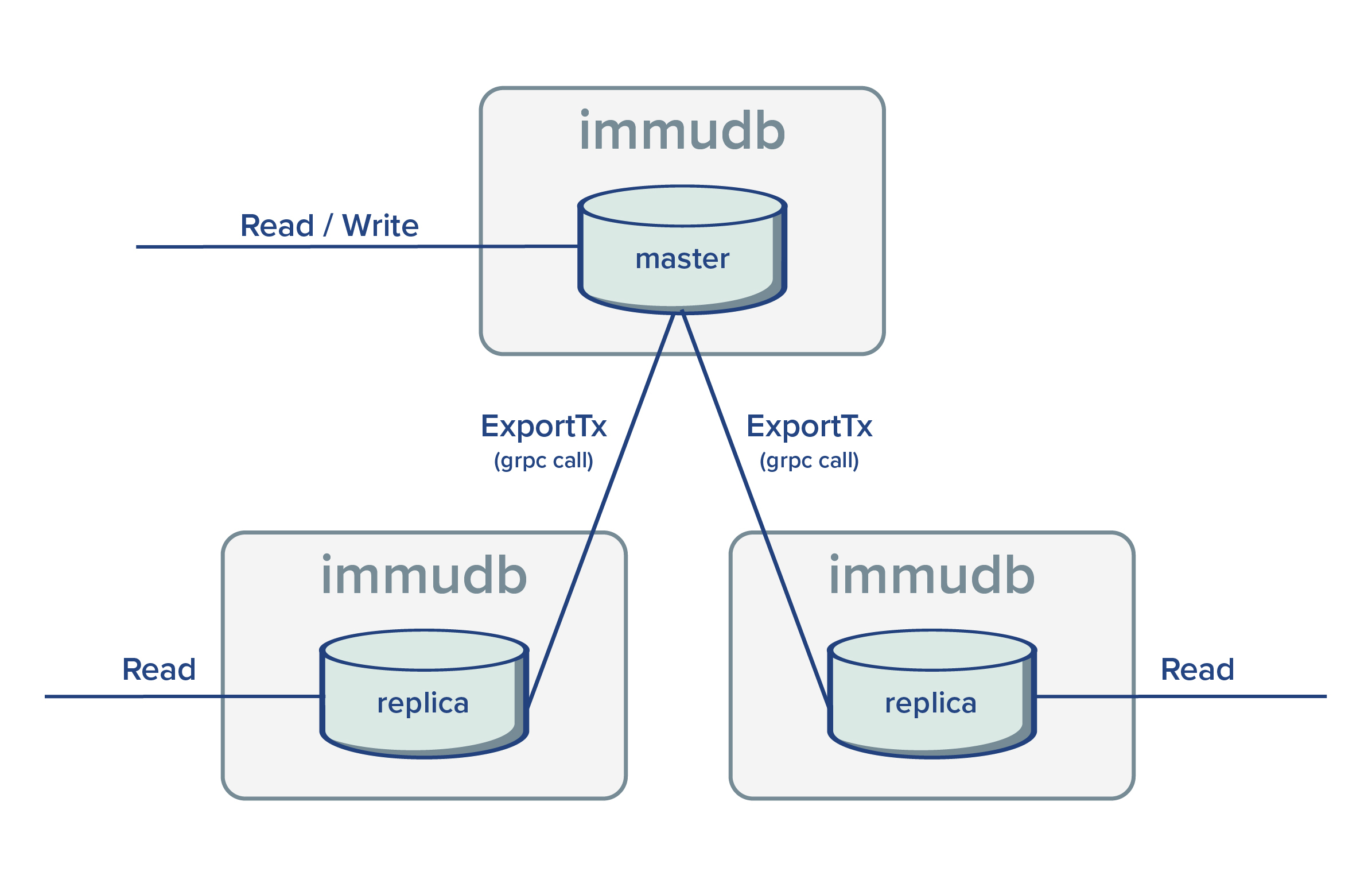
During replication, master databases have a passive role. The grpc endpoint ExportTx is used by replicas to fetch unseen committed transactions from the master.
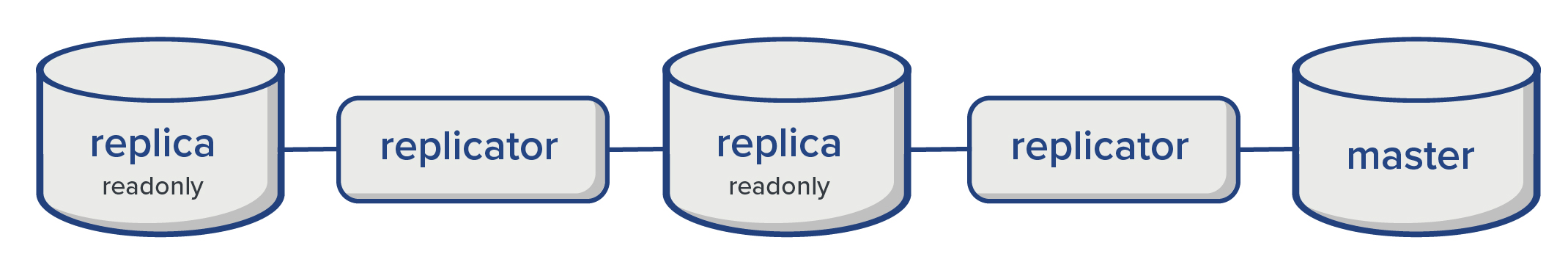
Replicas are read only and any direct write operation will be rejected. Using replicas allow to distribute query loads.
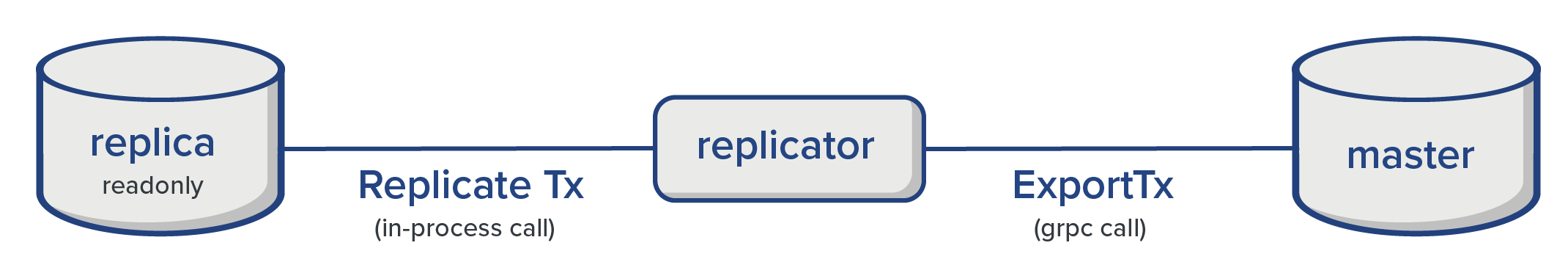
As shown in the diagram above, the replicator fetches committed transaction from the master via grpc calls. Internally, the replicator instantiates an immudb client (using the official golang SDK) and fetches unseen committed transactions from the master. In order to do so, the replicator requires valid user credentials with admin permissions, otherwise the master will reject any request.
Creating a replica
Creating a replica of an existent database using immuadmin is super easy:
$ ./immuadmin login immudb
Password:
logged in
$ ./immuadmin database create --replication-enabled=true --replication-follower-username=immudb --replication-follower-password=immudb --replication-master-database=defaultdb replicadb
database 'replicadb' {replica: true} successfully createdTIP
Display all database creation flags with
$ ./immuadmin help database createCreating a second immudb instance to replicate systemdb and defaultdb behaves similarly
Start immudb with enabled replication:
$ ./immudb --replication-enabled=true --replication-follower-password=immudb --replication-follower-username=immudb --replication-master-address=127.0.0.1TIP
Display all replication flags
$ ./immudb --helpIt's possible to create multiple replicas of a database. Each replica works independently of the others.
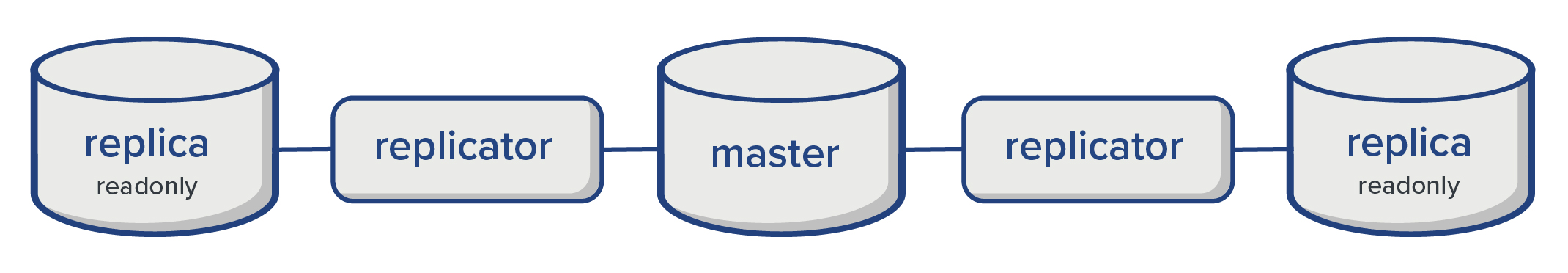
Given the master database acts in passive mode, there are no special steps needed in order to create more replicas. Thus, by repeating the same steps to create the first replica it's possible to configure new ones.
Replica of a replica
In case many replicas are needed or the master database is under heavy load, it's possible to delegate the creation of replicas to an existent replica. This way, the master database is not affected by the total number of replicas being created.
External replicator
By creating a database as a replica but with disabled replication, no replicator is created for the database and an external process could be used to replicate committed transactions from the master. The grpc endpoint ReplicateTx may be used to externally replicate a transaction.
Heterogeneous settings
Replication is configured per database. Thus, the same immudb server may hold several master and replica databases at the same time.